Why Switching to New Energy Vehicles Is Good for the Earth

New energy vehicles offer a practical solution for reducing harmful emissions. Battery electric vehicles produce 60%–69% fewer greenhouse gases than gasoline cars in the US and Europe.
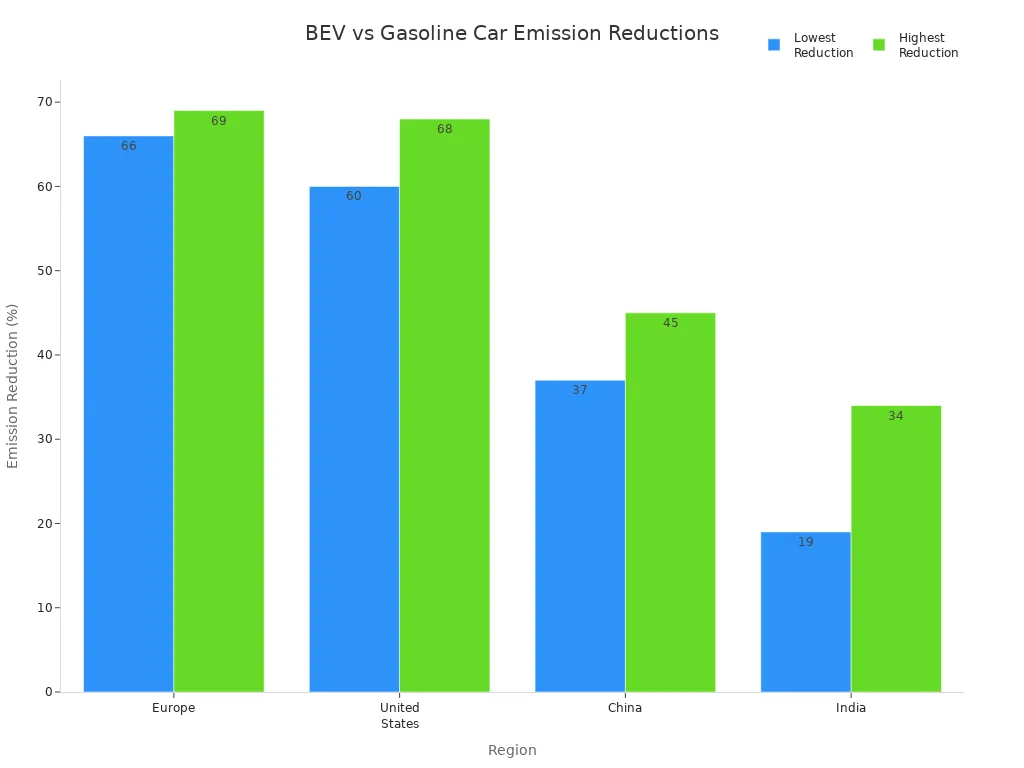
Cleaner transportation choices protect air quality and support public health.
Key Takeaways
- New energy vehicles cut harmful air pollution and prevent thousands of premature deaths in many cities by reducing tailpipe emissions.
- Switching to electric and hybrid vehicles lowers greenhouse gas emissions significantly, helping fight climate change and improving public health.
- Advances in battery recycling and renewable energy charging make new energy vehicles more sustainable and reduce their environmental impact.
New Energy Vehicles and a Cleaner, Healthier Environment

Reducing Air Pollution in Cities
Urban air pollution mainly comes from vehicles that burn fossil fuels. Cars, trucks, and buses release pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), and particulate matter (PM2.5) into the air. New energy vehicles help address this problem by using electric or hybrid powertrains, which either eliminate or greatly reduce tailpipe emissions. As a result, cities that adopt more electric vehicles see cleaner air and fewer harmful pollutants.
A peer-reviewed study published in Science of the Total Environment analyzed the effects of electric vehicle adoption on air quality and public health in major U.S. cities. The table below summarizes the impact:
| City | Impact on Premature Deaths (per month) | PM2.5 Change (μg/m3) | Ozone Level Change (ppb) | Economic Impact (per day) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Houston | Prevents 157 premature deaths | PM2.5 dropped by up to 2.29 | Ozone levels dropped (14.00-32.34 ppb) | Savings of $51 million to $249 million (NY, Chicago, Houston combined) | Positive impact on air quality and health benefits |
| New York | Prevents 796 premature deaths | PM2.5 dropped by up to 2.29 | Ozone levels dropped (14.00-32.34 ppb) | Included in economic savings above | Significant health benefits |
| Chicago | Prevents 328 premature deaths | PM2.5 dropped by up to 2.29 | Ozone levels dropped (14.00-32.34 ppb) | Included in economic savings above | Significant health benefits |
| Los Angeles | Saves 104 lives at 29% EV share; full electrification may increase mortality | PM2.5 increased by up to 0.67 in some areas | Some areas saw increases in ozone (MDA8) | Potential economic loss up to $18 million | Unique meteorology and geography cause complex effects, including increased secondary aerosols |
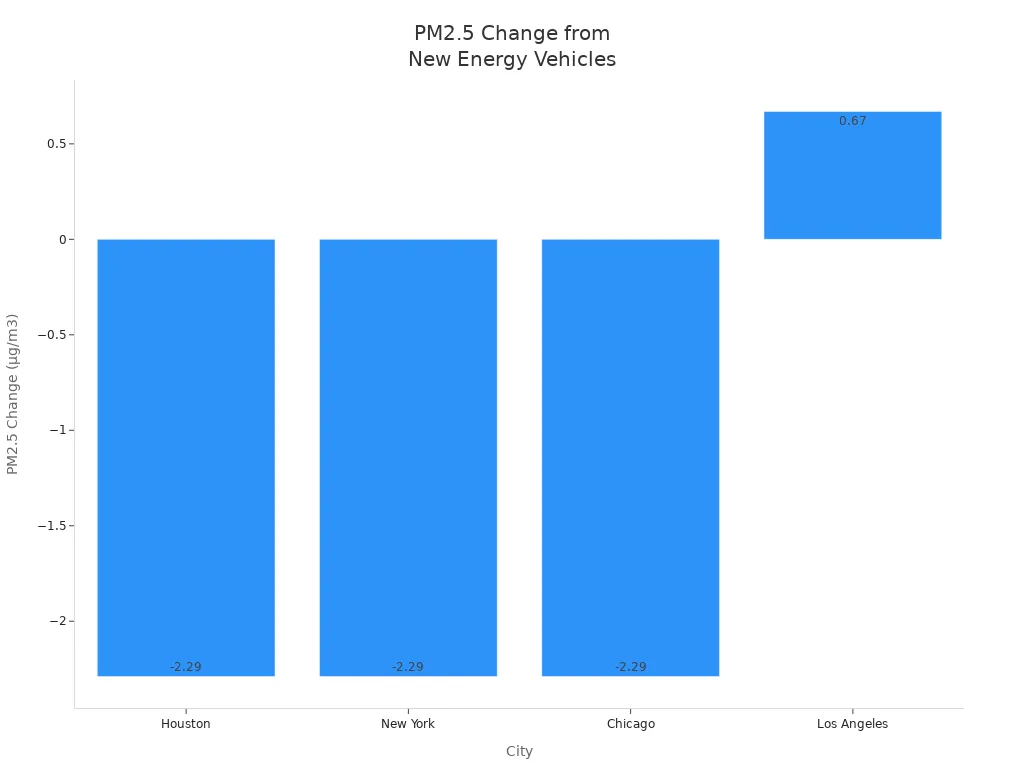
Most cities benefit from lower PM2.5 and ozone levels, which means cleaner air for everyone. However, local factors such as geography and weather can influence results, as seen in Los Angeles. Overall, new energy vehicles play a key role in reducing urban air pollution.
Improving Public Health and Quality of Life
Cleaner air leads to better health outcomes. When cities reduce vehicle emissions, residents experience fewer respiratory problems and other health issues. For example, a California study found that areas with more zero-emission vehicles saw a 3.2% decrease in asthma-related emergency visits. Lower levels of nitrogen dioxide, a pollutant linked to traffic, also appeared in these neighborhoods.
Cities with high adoption rates of new energy vehicles have seen significant reductions in PM2.5 and ozone, preventing thousands of premature deaths and saving millions in healthcare costs.
The table below compares life cycle emissions for different vehicle types, highlighting the health benefits of switching to cleaner options:
| Vehicle Type | Total Lifecycle Emissions (tCO2e) |
|---|---|
| Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) | 39 |
| Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) | 47 |
| Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles (ICE) | 55 |
Switching to new energy vehicles not only improves air quality but also reduces noise pollution. Electric cars and buses operate more quietly than traditional vehicles, lowering urban noise levels and supporting better sleep and cardiovascular health. In Beijing, the economic benefits from improved public health due to new energy vehicle adoption reached nearly 1% of the city’s GDP, mainly from fewer cases of chronic bronchitis and avoided deaths.
Lowering Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Traditional vehicles emit large amounts of greenhouse gases, mainly through burning gasoline or diesel. These emissions contribute to climate change and global warming. New energy vehicles offer a solution by using electricity or alternative fuels, which can significantly cut greenhouse gas output.
- Electric vehicles are up to 88% less greenhouse gas intensive than gasoline vehicles in some regions.
- Lifetime emissions of electric vehicles are less than half those of gasoline or diesel cars, especially as the electric grid becomes cleaner.
- Advances in battery production and recycling, along with more renewable energy in the grid, continue to lower the carbon footprint of new energy vehicles.
The chart below shows the emissions reduction across different vehicle categories:
Electric vehicles may have higher emissions during manufacturing, mainly due to battery production. However, they quickly offset this with zero tailpipe emissions during use. In most cases, electric vehicles reach carbon parity with traditional vehicles after about one year of driving. As more renewable energy sources power the grid, the environmental benefits of new energy vehicles will only increase.
New Energy Vehicles: Addressing Environmental Concerns and Maximizing Benefits

Battery Production and Recycling Improvements
Manufacturers have made significant progress in reducing the environmental impact of battery production for new energy vehicles. They now prioritize sustainable raw material sourcing, responsible mining, and ethical supply chains. Advances include the use of alternative materials, improved extraction techniques, and research into solid-state batteries that require fewer scarce resources. Many factories integrate renewable energy sources like solar and wind to lower carbon emissions. Energy-saving technologies and process optimization further improve efficiency and reduce waste. Battery recycling infrastructure has expanded, with batteries designed for easier disassembly and reuse, promoting a circular economy.
| Metric | 2023 Result | 2024 Result |
|---|---|---|
| Collection Rate (%) | 68% | 72% |
| Recycling Rate (%) | 85% | 88% |
| Reduction in Landfill (tons) | 800 | 900 |
Recycling batteries uses less energy than producing new ones, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and prevents toxic substances from contaminating the environment.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Charging
Integrating renewable energy into charging infrastructure maximizes the benefits of new energy vehicles. Solar and wind power at charging sites reduce transmission losses and lower carbon emissions. Second-life EV batteries in charging stations can save up to $25 billion annually by 2040 and cut CO2 emissions by 16 megatons per year. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology allows vehicles to store and supply energy, improving grid resilience and reducing costs. Smart charging platforms prioritize renewable energy use, increasing site capacity and energy resilience.
Clearing Up Common Misconceptions
Several misconceptions surround new energy vehicles. Some believe EVs are as harmful as conventional cars due to manufacturing emissions, but studies show that in 95% of the world, EVs have a lower lifetime carbon footprint. Others worry about battery disposal, yet recycling rates are rising and valuable materials are recovered. Concerns about battery lifespan are addressed by data showing minimal degradation over long distances, and global reserves of lithium and cobalt are sufficient for future demand. Most EV batteries do not use rare earth elements, and recycling technology continues to improve.
Switching to new energy vehicles offers a practical way to protect the planet. Norway’s widespread adoption shows real improvements in air quality and emissions.
- Electric vehicles reduce air and noise pollution.
- Expert organizations and agencies confirm their long-term sustainability benefits.
Every step toward greener vehicles creates a healthier future for all.
FAQ
What is a new energy vehicle?
A new energy vehicle uses electricity, hydrogen, or hybrid systems for power. These vehicles produce fewer emissions than traditional gasoline or diesel cars.
How long do electric vehicle batteries last?
Most electric vehicle batteries last 8–15 years. Manufacturers often provide warranties. Battery technology continues to improve, increasing lifespan and reliability.
Are charging stations widely available?
Charging stations continue to expand in cities and along highways. Many public places, workplaces, and shopping centers now offer charging options for electric vehicles.
Tip: Drivers can use mobile apps to locate nearby charging stations quickly.