The Tech Behind the Seed How Optical Sorters Guarantee Quality
Optical sorters use high-resolution cameras and AI algorithms to scan every seed at high speed. This technology instantly removes defects and impurities with precise pneumatic jets. A sesame seeds optical sorter achieves a purity level impossible with manual methods. The technology's market growth underscores its value.
- The global optical sorter market is projected to reach USD 4.1 billion by 2027.
- It is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.9%.
How a Sesame Seeds Optical Sorter Works

The journey from a mixed batch of seeds to a uniformly pure product is a marvel of modern technology. A sesame seeds optical sorter executes a sophisticated four-step process with incredible speed and accuracy. This system guarantees that every single seed meets stringent quality standards before it proceeds to packaging.
Step 1: Uniform Feeding
The process begins with the uniform feeding of sesame seeds into the machine. A vibratory feeder ensures the seeds flow steadily and in a single layer down specialized channels or chutes. This controlled distribution is critical for the subsequent steps.
- Enclosed Feeding System: Many modern sorters feature an enclosed feeding system. This design provides superior chute protection and ensures a more consistent, uninterrupted flow of seeds.
- No Overlap: Spreading the seeds evenly prevents them from clumping or overlapping. This separation allows the imaging system to capture a clear view of each individual seed.
The machine's throughput, or the volume of seeds it can process, is a key performance metric. Different models offer varying capacities to meet diverse production demands.
| Model | Throughput (Tons/Hour) |
|---|---|
| ZF300 | 1.0–3.0 |
| ZF500 | 2.0–5.0 |
| ZF700 | 3.0–8.0 |
Step 2: High-Definition Imaging
As the seeds free-fall through the inspection zone, high-resolution cameras capture detailed images from multiple angles. This stage acts as the machine's eyes, scrutinizing every seed with superhuman precision.
Note: The imaging system uses advanced lighting to reveal defects that are invisible to the naked eye. Energy-efficient LED illumination is standard, providing intelligent and flexible backlighting that enhances the visibility of discoloration, foreign materials, and other imperfections.
Specialized cameras, some boasting resolutions over 5400 pixels, generate a massive stream of visual data. These full-color RGB cameras work alongside other sensors, such as near-infrared (NIR) or laser scanners, to gather comprehensive information about each seed's color, shape, size, and even internal composition.
Step 3: AI-Powered Analysis
This is where the machine's intelligence comes into play. The captured images are instantly processed by a powerful onboard computer running sophisticated AI algorithms. This digital brain analyzes the data and makes a split-second "accept" or "reject" decision for every seed.
The system employs advanced machine learning models to achieve this.
- Deep Learning: This cutting-edge approach uses neural networks, like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), trained on millions of images. The AI learns to identify subtle patterns associated with defects such as small disease spots, insect damage, or slight discoloration.
- Multi-Attribute Analysis: The AI does not just look at color. It combines data on shape, size, and texture to differentiate between a discolored seed and a foreign object like a tiny stone. This comprehensive analysis allows the sesame seeds optical sorter to detect a wide range of impurities with unparalleled accuracy.
Operators can fine-tune these sorting parameters through an intuitive software interface. They can define the acceptable criteria for color, size, and shape, customizing the machine's performance to meet specific quality targets.
Step 4: Precise Ejection
The final step is the physical separation of rejected seeds. Once the AI identifies a defective seed or foreign particle, it calculates its exact position and trajectory. It then triggers a bank of high-speed pneumatic ejectors, or air jets.
Tip: The speed of these ejectors is astonishing. Advanced systems feature response times as low as 0.8 milliseconds, with some intelligent solenoid valves reacting in just 0.05 milliseconds.
A precise, powerful puff of compressed air strikes the unwanted particle, knocking it out of the main stream and into a rejection bin. The good, accepted seeds continue their path undisturbed, flowing into a separate collection chute. This entire process, from imaging to ejection, happens in the blink of an eye, ensuring both high purity and maximum efficiency. For a sesame seeds optical sorter to maintain its peak performance and longevity, which can range from 5 to 10 years, regular maintenance such as cleaning glass windows and testing air valves is essential.
The Technological Edge in Quality Control

Optical sorters provide a decisive technological advantage in modern food processing. They elevate quality control beyond human capability through a combination of artificial intelligence, incredible speed, and sophisticated defect detection. This technology is not just an improvement; it is a transformation of industry standards.
Superior Accuracy with AI
Artificial intelligence gives optical sorters a level of precision that manual inspection cannot match. Human sorting is prone to fatigue, subjectivity, and error. AI-powered systems, in contrast, deliver consistent and objective results 24/7.
AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, learn to identify defects from vast datasets of images. For example, AI-powered systems sorting maize ears demonstrate an average accuracy of 96.25%. This capability allows a machine to distinguish between a healthy seed and one with subtle discoloration or insect damage. The AI's learning ability continuously refines its performance. Advanced software, such as Cimbria's BRAIN, autonomously adjusts sorting parameters, creating complex "recipes" that optimize purity and reduce the need for human guesswork.
The result is an exceptionally pure final product. Top-tier optical sorters can achieve a purity level of 99.99% for products like sesame seeds, a standard that is virtually unattainable through manual methods.
Leading manufacturers like TOMRA, Bühler, and Satake are pioneers in this space, developing AI-driven systems that set new benchmarks for accuracy across the agricultural industry.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
The operational speed of optical sorters creates a massive leap in productivity. A single machine can process thousands of individual seeds per second, a volume that would require a large team of manual laborers. This efficiency directly translates into significant cost savings and a rapid return on investment.
| Sorting Method | Items Per Minute | Accuracy Rate |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Optical Sorting | Up to 200 | Exceeding 95% |
| Traditional Manual Sorting | 30-40 | 65-80% |
The economic benefits are clear. Automated systems can reduce labor costs by 80-90%. For a rice mill, this can mean lowering the labor cost per ton from over $12 to just over $2. Many companies find that the savings from reduced waste and labor allow the optical sorter to pay for itself within 12 to 18 months.
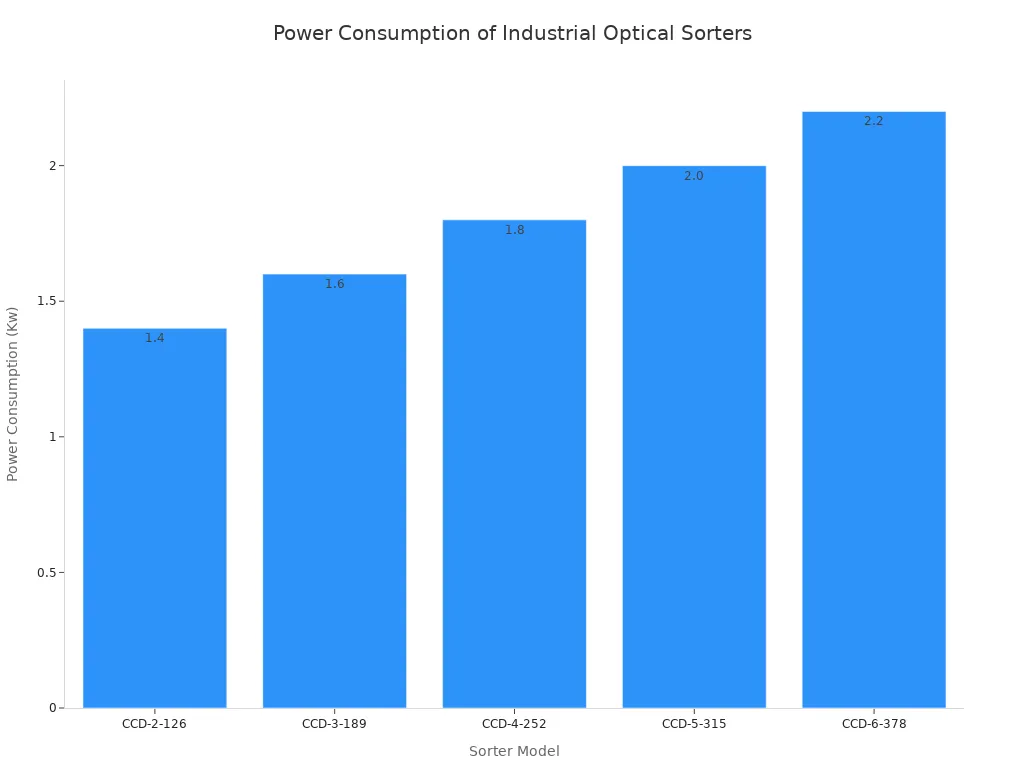
Furthermore, modern machines are designed for energy efficiency. Many models operate on surprisingly low power, minimizing their environmental footprint and operational costs.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) further enhances efficiency. IoT connectivity enables:
- Remote Monitoring: Technicians can diagnose issues from anywhere, reducing downtime.
- Predictive Maintenance: The system analyzes performance data to predict and prevent potential failures.
- Real-time Analytics: Operators gain immediate insights to optimize sorting performance.
Advanced Defect Detection
Modern optical sorters see far more than the human eye. Using a combination of high-resolution RGB cameras and multispectral imaging technologies like near-infrared (NIR) and short-wave infrared (SWIR), these machines can identify a vast range of defects. A high-performance sesame seeds optical sorter can detect issues based on color, shape, size, and even chemical composition.
Common foreign materials easily removed include:
- Stones, glass, and sticks
- Other grains or foreign seeds
- Sclerotia and xanthium seeds
Beyond obvious contaminants, the technology excels at identifying subtle product flaws. Multispectral imaging allows the sorter to detect defects that are invisible under normal light. By analyzing how seeds reflect light at different wavelengths, the system can spot:
- Fungal infections like Fusarium
- Internal insect damage
- Rancidity or heat damage
- Micro-sized black spots (as small as 0.01mm²)
This ability to analyze spectral signatures is a game-changer. It allows processors to identify and remove compromised seeds, ensuring the final product is not only pure but also safe.
The fusion of high-speed imaging, AI analysis, and precise ejection makes optical sorters essential technology. These systems establish the new industry benchmark for quality. A modern sesame seeds optical sorter guarantees exceptional purity and safety, helping products meet strict international standards and building consumer trust in the global food supply.
FAQ
Can one sorter handle different types of seeds?
Yes. Operators create and save sorting programs for different seeds. The machine's software allows quick adjustments to its parameters, ensuring flexibility for various products and quality standards.
How does an optical sorter improve food safety?
The technology removes harmful contaminants like stones, glass, and mycotoxin-affected grains. This process significantly reduces health risks and ensures the final product meets stringent safety regulations.
What is the typical lifespan of an optical sorter?
A well-maintained optical sorter typically has a lifespan of 5 to 10 years. Regular cleaning and preventive maintenance are crucial for maximizing its operational life and performance.
See Also
Capsule Sorters: Essential Technology for Flawless Product Defect Elimination
Sterile Filter Devices: How They Function to Ensure Product Purity
Top Capsule Checkweighers for Buyers to Evaluate in the Year 2025
Defining Pharmaceutical Checkweighers: Key Characteristics and Vital Functions Explained
Three Must-Have Industrial Checkweighers for Every Modern Food Processing Plant