The Future of Stainless Steel Wire Rope Is Here

The evolution of stainless steel wire rope is accelerating. New material alloys, innovative construction designs, and integrated smart technologies are driving this transformation. These advancements provide unprecedented strength, superior corrosion resistance, and real-time monitoring for safety-critical applications. The industry's rapid adoption of these innovations is reflected in strong market growth projections.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Projected CAGR (2025-2033) | 6.71% |
This progress sets a new standard for performance and reliability across demanding sectors.
Key Takeaways
- New stainless steel wire ropes are much stronger and resist rust better. They use new materials and designs.
- Special alloys like duplex stainless steel are very strong. They can handle harsh places like the ocean.
- New ways to build ropes make them last longer. They are also stronger and smoother.
- Smart ropes have sensors inside them. These sensors watch the rope in real-time to prevent problems.
- Digital twins are like virtual copies of ropes. They help predict when a rope needs care or replacement.
Advanced Material Science: The New Generation of Alloys
The foundation of a superior wire rope lies in its material composition. Modern metallurgy is pushing the boundaries of what stainless steel can achieve. Scientists and engineers are developing new alloys that deliver exceptional performance, moving far beyond traditional grades. These next-generation materials provide the core strength and resilience needed for the most demanding industrial environments.
High-Performance Duplex and Super Duplex Alloys
Duplex and super duplex stainless steels represent a significant leap forward in material technology. These alloys possess a dual-phase microstructure of both austenite and ferrite, which gives them a powerful combination of strength and corrosion resistance. This makes them ideal for a high-performance stainless steel wire rope. Compared to the widely used 316-grade stainless steel, the advantages are clear.
| Property | Duplex Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Higher yield and tensile strength | Lower yield and tensile strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | More resistant to corrosion and cracking | Less resistant to corrosion and cracking |
The superior performance of duplex alloys comes from their specific chemical makeup. They contain higher levels of chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen. This composition can double the yield strength compared to standard grades. It also provides outstanding resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, especially in chloride-rich environments like offshore platforms and chemical processing plants.
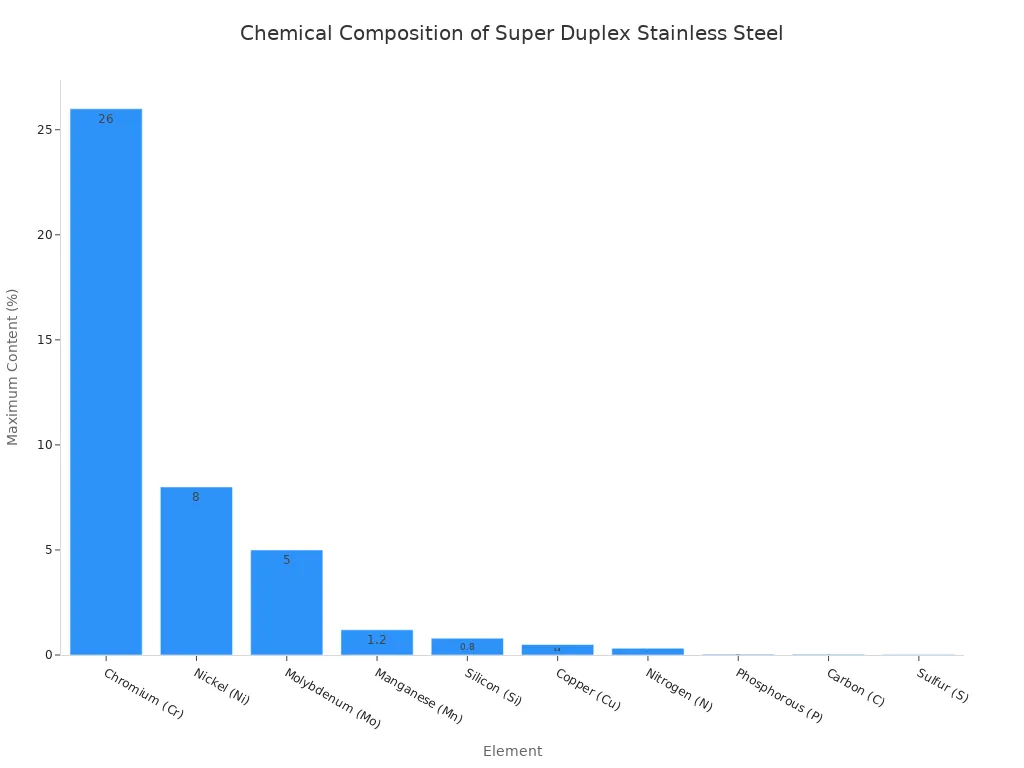
Super duplex grades, such as 2507, take this performance even further. Their composition is precisely controlled to maximize durability.
- It contains approximately 25% chromium, 4% molybdenum, and 7% nickel.
- It has a very low carbon content, typically below 0.03%.
The typical chemical composition of super duplex steel highlights the elements responsible for its elite status.
Precipitation-Hardening (PH) Stainless Steels
Precipitation-hardening (PH) stainless steels offer another path to extreme strength. These alloys gain their impressive mechanical properties through a heat treatment process. This process causes microscopic particles to form within the metal's structure, obstructing internal movement and dramatically increasing strength and hardness.
Recent breakthroughs in material science are unlocking even greater potential. Researchers have developed a fatigue-resistant stainless-steel alloy with remarkable properties. By cyclically twisting conventional steel, they created a material with double the yield strength and up to 10,000 times the resistance to metal fatigue. This innovation promises to revolutionize components in aerospace, nuclear reactors, and other high-stress applications.
Innovation at the Nanoscale 🔬 The integration of nanomaterials is also transforming stainless steel. These microscopic additions create alloys with unique capabilities.
- They provide anticorrosive properties comparable to titanium, offering a cost-effective solution for new energy sectors.
- They improve antifouling characteristics, which is critical for marine and biomedical applications.
- They enhance the strength-to-weight ratio, allowing manufacturers to create stronger products with less material.
These advanced alloys are not just theoretical concepts. They are the building blocks for the stronger, safer, and more durable wire rope systems that modern industries demand.
Innovative Construction for a Better Stainless Steel Wire Rope

Advanced alloys provide a strong foundation. Innovative construction methods build upon it to unlock new levels of performance. The helical structure of a wire rope, with its multiple wires and strands, inherently shares loads to ensure reliability. Modern manufacturing techniques refine this principle. They enhance strength, increase durability, and improve resistance to abrasion, bending, and crushing. These construction advancements make wire rope a more versatile and adaptable solution across industries.
Compacted and Swaged Rope Constructions
Compaction and swaging are manufacturing processes that reshape the rope's internal geometry. These techniques compress the round strands of a standard rope. The process flattens the outer wires and reduces internal voids. This creates a smoother rope surface with a denser cross-section.
More Steel, More Strength 💪 The primary goal is to increase the rope's fill factor, or density. Traditional rope constructions fill about 58% of their diameter with steel. Compacted ropes can achieve a fill factor of up to 80%. This represents a nearly 38% increase in metallic area, which directly boosts the rope's breaking strength.
This denser profile offers several key advantages:
- Increased Strength: A larger metallic area results in a higher breaking force for the same diameter.
- Enhanced Durability: The smooth surface reduces friction and wear on sheaves and drums.
- Longer Fatigue Life: Improved inter-wire contact lowers internal stress, extending the rope's service life in high-cycle applications.
Plastic-Impregnated and Coated Ropes
Engineers use plastic coatings and impregnation to shield a stainless steel wire rope from harsh operational hazards. Plastic impregnation (PI) injects a polymer, like polypropylene, between the inner and outer strands. This process locks out corrosive agents, reduces internal friction, and maintains the rope's structural integrity.
External plastic coatings offer another layer of defense. Materials are chosen based on the application's specific demands.
| Coating Type | Key Advantages | Primary Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl (PVC) | Cost-effective; Excellent protection against moisture and chemicals; Provides a smooth, safe surface. | Can degrade with prolonged UV exposure; Not for high-heat environments. |
| Nylon | Superior abrasion and wear resistance; Better performance against UV and mechanical stress. | Can become brittle in extreme cold; Higher cost than PVC. |
These polymer layers are critical in marine environments. They protect against saltwater and UV rays, ensuring extended reliability for mooring, anchoring, and winching. The coating also adds flexibility and makes the rope safer to handle by reducing the risk of frayed wires.
Smart Rope Technology: Integrating IoT for Predictive Safety
The integration of smart technology is transforming wire rope from a passive component into an active, data-generating asset. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, creating a new paradigm for safety and operational efficiency. Industry leaders are already embracing this shift. For instance, Pelican Rope Works has partnered with Scope, a provider of AI-robotic inspection systems, to integrate intelligent diagnostics into their products. This collaboration leverages computer vision to detect wear and provide comprehensive digital inspection records, revolutionizing how rope integrity is monitored.
Fiber Optic Sensing Integration
Fiber optic sensing embeds intelligence directly into the core of a wire rope. This technology uses light signals traveling through hair-thin glass fibers to measure physical changes with incredible precision. The primary method involves Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensors. These microscopic gratings reflect specific wavelengths of light. Any stretching, compression, or temperature change alters the reflected light, providing immediate data on the rope's condition.
Engineers use FBG sensors to monitor multiple variables simultaneously.
- Strain and Stress: FBG force-sensing elements, installed on an internal steel strand, monitor axial strain to characterize the overall stress state of the cable.
- Wire Breaks: FBG vibration sensors, combined with a convolutional neural network, analyze vibration signals. The system learns the rope's normal vibration signature and can instantly identify the unique signal created by a wire break.
- Temperature Compensation: A single fiber can contain both a strain grating and a temperature compensation grating. This dual-sensor setup allows the system to distinguish between strain from mechanical load and expansion from temperature changes, ensuring measurement accuracy.
This technology has proven its value in preventing catastrophic failures across several industries. A field study in Guangdong, China, used a distributed fiber optic system to monitor a 32 km overhead power line, detecting strain changes as small as 0.0002% caused by weather. This demonstrates the system's ability to identify localized stress before it leads to damage. Other successful applications include:
- Elevator Modernization: Real-time tension data helps technicians identify and correct imbalances, significantly reducing downtime and enhancing passenger safety.
- Construction Site Cranes: Sensors allow operators to maintain proper rope tension, preventing overload and optimizing lifting cycles for improved efficiency.
- Mining Operations: Continuous monitoring in lifting and hauling applications helps prevent rope breakage, a major cause of costly downtime and safety hazards.
RFID and Digital Twinning for Lifecycle Management
While fiber optics provide real-time internal data, other technologies manage a rope's entire lifecycle. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) and digital twinning create a comprehensive "birth-to-retirement" record for every asset. This approach replaces error-prone manual logs with a reliable, automated system.
RFID technology assigns a unique digital identity to each stainless steel wire rope. The process is straightforward and effective:
- An RFID chip with a unique serial number is embedded in or attached to the rope.
- Field personnel use a reader to scan the chip, which synchronizes with a secure, cloud-based database.
- The database provides instant access to the rope's complete history, including inspection records, maintenance logs, test results, and certifications.
This digital logbook is the foundation for a more advanced concept: the digital twin. A digital twin is a virtual, dynamic model of a physical wire rope. It uses real-world data to simulate the rope's condition, predict its behavior, and forecast its remaining service life. Creating an effective digital twin requires integrating multiple data inputs, such as:
- Temperature
- Vibration
- Pressure
- Tension and elongation
- Wear patterns
Predictive Power in Action 💡 The digital twin combines these live sensor inputs with physics-based models and historical degradation curves. AI systems analyze this rich dataset to identify early signs of fatigue or structural weakness. This allows asset managers to move from reactive repairs to proactive, predictive maintenance, scheduling replacements only when necessary and maximizing both safety and operational uptime. The collaboration between Scope and early adopter MYR Group was crucial in pressure-testing and validating this AI-driven approach, achieving high accuracy in detecting rope damage in real-world conditions.
Application Spotlight: Where New Solutions Make a Difference

Advanced alloys and smart technologies are not just theoretical improvements. They are actively solving complex challenges in the world's most demanding industries. These innovations deliver tangible benefits in safety, efficiency, and operational longevity where performance is non-negotiable.
Heavy-Duty Lifting and Cranes
The heavy lifting industry relies on absolute rope integrity. Compacted and super duplex ropes are now essential components in high-capacity cranes, boosting their lifting capabilities.
- Tower cranes
- Crawler cranes
- Mobile cranes
Beyond raw strength, smart technology provides critical operational intelligence. For example, Konecranes Rope Analysis uses 3D modeling to assess the exact condition and remaining design life of a rope. This data-driven approach optimizes change intervals, preventing both premature replacements and catastrophic failures that cause significant downtime.
Safety-Critical Architectural Systems
Modern architecture increasingly uses stainless steel wire rope for both structural support and aesthetic appeal. These systems appear in everything from tensioned roof structures and suspension bridges in eco-parks to skyscrapers with suspended sun shades. Because these are public-facing structures, safety is paramount.
Code and Compliance 📜 Architectural applications are governed by strict safety standards, such as ASME B30.5. These regulations mandate specific design factors, material traceability, and inspection protocols. For instance, suspension ropes must often have a design factor of at least 10, ensuring they can handle loads far exceeding their rated capacity.
Offshore and Marine Operations
The offshore environment is relentlessly corrosive. Plastic-impregnated ropes provide a powerful defense for mooring lines and winching systems. The polymer filling shields the rope's core from saltwater and abrasive particles, preventing internal deterioration and extending its working life. This design also reduces wear on drums and sheaves, lowering maintenance costs. Specialized equipment, like Mammoet's 800t linear winches, leverages advanced hydraulic monitoring and innovative designs to further reduce downtime and increase efficiency in demanding offshore services.
Key innovations are setting a new standard for the modern stainless steel wire rope. Advanced alloys provide superior corrosion resistance, while new constructions enhance strength. These solutions actively solve real-world challenges in heavy-duty and safety-critical industries today. The integration of smart technology and AI-driven platforms ensures this evolution continues.
The industry is moving decisively toward a future of smarter, stronger, and safer wire rope systems that deliver unparalleled performance and reliability.
FAQ
What makes duplex alloys better than traditional stainless steel?
Duplex alloys possess a dual-phase microstructure. This structure provides significantly higher tensile strength and superior resistance to corrosion, especially in chloride-rich environments. Their advanced composition makes them far more durable than standard grades like 316 stainless steel for demanding applications.
Why are some wire ropes coated in plastic?
Plastic coatings and impregnation provide a critical protective barrier. This technology serves several key functions:
- It shields the rope from moisture and chemicals.
- It reduces internal friction and abrasion.
- It improves handling safety by covering wires.
How does a "smart rope" prevent failures?
A smart rope uses integrated sensors, like fiber optics, to monitor its condition in real time. The system detects stress, strain, and wire breaks as they happen. This data allows operators to predict potential issues and prevent failures before they occur.
What is a digital twin for a wire rope?
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical wire rope. It uses live sensor data and historical information to simulate the rope's condition. This model helps asset managers predict the rope's remaining service life and schedule maintenance proactively. 💻
See Also
Optimizing Steel Processing for Heat Exchangers: Consistent Performance and Reliable Outcomes
Assessing Molybdenum Plugs' Role in Seamless Steel Pipe Manufacturing by 2025
Cutting-Edge Materials: Transforming the Future of Heat Exchanger Supply Chains
Essential WT20 Thoriated Tungsten Electrode Insights for Superior TIG Welding
Steel vs. Wood Support Columns: A Comprehensive Look at Pros and Cons