Understanding 2507 The Ultimate Corrosion Fighter

2507 super duplex stainless steel earns its reputation as an ultimate corrosion fighter. Its specialized chemical recipe contains high levels of chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen. This composition creates a balanced two-phase microstructure. This structure gives materials like a 2507 S32750 Super Duplex Round Bar exceptional defense against pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking. It performs reliably in aggressive environments such as seawater and chemical processing plants, where standard materials fail.
Key Takeaways
- 2507 super duplex steel fights corrosion very well. It has special ingredients like chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen. These make it strong against rust and cracks.
- This steel has a special two-part structure. This structure makes it both strong and tough. It works well in harsh places like seawater.
- 2507 steel is much stronger than regular stainless steel. It also resists rust better. This is why it is used in tough jobs like oil rigs and chemical plants.
- Using 2507 steel costs more at first. But it lasts a long time. It needs fewer repairs. This saves money over many years.
What Defines 2507 Super Duplex Steel?

The exceptional performance of 2507 super duplex steel stems from two core characteristics: its precise chemical composition and its unique internal structure. These elements work together to create a material perfectly engineered for harsh conditions.
The Chemical Recipe for Resistance
The alloy's power begins with a specific blend of elements. High concentrations of chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen are the primary drivers of its corrosion-fighting ability. Industry standards define these critical components within tight ranges to guarantee performance.
| Element | Percentage Range (%) |
|---|---|
| Chromium (Cr) | 24.0–26.0 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 3.0–5.0 |
| Nitrogen (N) | 0.24–0.32 |
This enriched formula sets the material apart from other duplex grades. For instance, when compared to the common 2205 grade, 2507 contains significantly higher levels of these key corrosion-resistant elements.
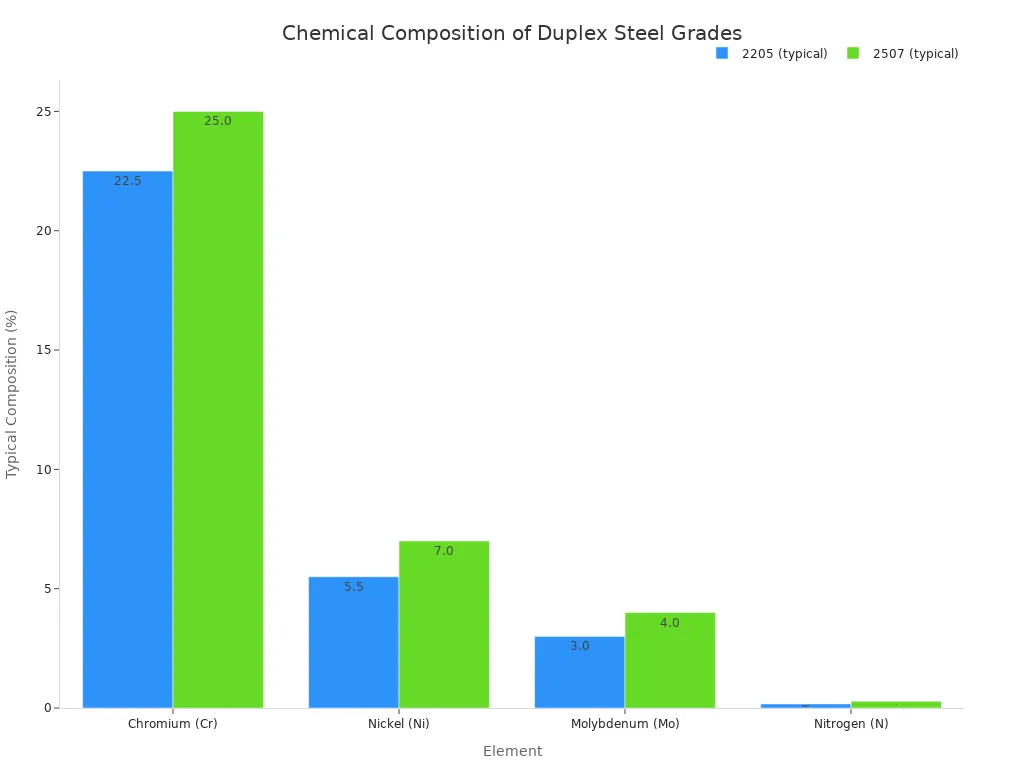
The Two-Phase Microstructure Advantage
Beyond its chemistry, the steel's internal structure provides a distinct advantage. It possesses a balanced two-phase microstructure, containing nearly equal parts of austenite and ferrite.
What does this mean? 💡 This dual structure combines the best properties of both phases. The ferritic portion provides high strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking, while the austenitic portion delivers excellent toughness and general corrosion resistance.
This balanced composition is not an accident. Engineers design this structure to maximize performance. The combination of the austenitic and ferritic phases effectively interrupts the progression of cracks. This mechanism gives the material its superior defense against stress corrosion cracking, a common failure mode in chloride-rich environments. The result is a robust material that maintains its integrity where others would fail.
Key Performance Properties of 2507
The reputation of 2507 super duplex steel is built on a foundation of measurable and exceptional performance characteristics. Its advanced chemistry and microstructure translate directly into superior mechanical strength, quantifiable corrosion resistance, and a reliable operational temperature range. These properties make it the material of choice for the most demanding industrial applications.
Superior Mechanical Strength
Super duplex steel 2507 exhibits remarkable mechanical strength, often double that of standard austenitic stainless steels like 316L. This high strength-to-weight ratio provides a significant design advantage. Engineers can use thinner sections of the material without compromising structural integrity. This capability leads to lighter-weight components and potential cost savings in both material and supporting structures.
The alloy achieves impressive yield strengths around 550 MPa (80 ksi) and tensile strengths exceeding 800 MPa (116 ksi). This high strength ensures components can withstand extreme pressures and heavy mechanical loads.
| Property | Value (ksi) | Value (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Yield Strength (0.2%) | 80 | 550 |
| Minimum Tensile Strength | 116 | 800 |
This inherent strength, combined with its excellent corrosion resistance, provides a level of reliability that other materials cannot match in aggressive service conditions.
Corrosion Resistance Metrics (PREN)
Engineers use a specific metric to predict and compare the pitting corrosion resistance of stainless steels. This metric is the Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN). A higher PREN value indicates greater resistance to localized pitting corrosion, particularly from chlorides.
How is PREN calculated? 💡 The industry standard formula for duplex stainless steels is:
PREN = %Cr + 3.3(%Mo) + 16(%N)This formula shows how chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), and nitrogen (N) each contribute to the steel's defensive capabilities.
With its enriched chemical composition, 2507 super duplex steel achieves a PREN value that is significantly higher than other common alloys. This superior rating confirms its status as a top performer in chloride-rich environments.
| Alloy Type | Typical PREN Value |
|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | 25 |
| 2205 Duplex Steel | 35 |
| 2507 Super Duplex Steel | ≥ 42 |
This high PREN value translates directly to dependable performance in applications like subsea equipment and desalination plants, where resistance to pitting is critical for long-term service life.
Safe Operating Temperature Range
The two-phase microstructure of this super duplex steel dictates its effective operating temperature range. The material maintains its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance at temperatures up to 300°C (572°F).
However, prolonged exposure to temperatures above this limit can lead to the formation of brittle phases within the microstructure. This change can reduce the material's toughness and corrosion resistance. At the lower end, the alloy maintains good toughness down to -50°C (-58°F), though it may experience a ductile-to-brittle transition at very low cryogenic temperatures. Operating within this defined temperature window is essential to ensure the material delivers its full performance potential.
Where is 2507 Used?

The exceptional properties of 2507 super duplex steel make it indispensable in industries where material failure is not an option. Its combination of high strength and superior corrosion resistance allows it to perform reliably in some of the world's most hostile environments. Engineers specify this alloy for critical applications across the oil and gas, marine, and chemical processing sectors.
Oil & Gas Subsea Equipment
The deep-sea oil and gas industry operates under extreme conditions. High pressures, low temperatures, and constant exposure to corrosive seawater create a challenging environment for any material. Super duplex steel excels here, providing the necessary durability for long-term subsea installations. Its high strength allows for lighter components, a significant advantage in deep-water projects.
Case in Point: A Canadian oil company successfully used Super Duplex Stainless Steel 2507 for a pipeline in an offshore oil field near Newfoundland. This choice directly addressed the severe challenge of seawater corrosion, proving the material's value in deep-water applications.
Common subsea equipment benefiting from this advanced alloy includes:
- Subsea manifolds and pipelines
- Flowlines and risers
- Umbilicals and mooring systems
- Subsea connectors
Marine and Desalination Plants
Marine environments and desalination processes present a constant battle against chloride-induced corrosion. Seawater reverse osmosis (RO) plants, in particular, require materials that can withstand high-salinity water at extreme pressures. The 2507 alloy is an ideal solution for these demanding conditions.
Key components in high-pressure pumps for seawater RO systems are often constructed from this super duplex steel. Its robust nature ensures reliable operation and extends the service life of critical equipment. The material is frequently used for:
- High-pressure piping and vessels handling seawater and brine
- Pump components and casings exposed to aggressive flows
- Systems operating in high-salinity and high-pressure conditions
Aggressive Chemical Processing
Chemical processing plants handle a wide range of corrosive substances, from strong acids to chloride-rich solutions. The super duplex structure of 2507 provides outstanding performance in these extremely harsh environments. It demonstrates excellent resistance to uniform corrosion from inorganic acids like sulfuric and hydrochloric acid, even when contaminated with chlorides.
Did You Know? 💡 This steel grade shows high resistance to organic acids, such as those found in terephthalic acid plants. Its performance makes it a competitive choice over many high-alloyed austenitic and nickel alloys.
Its ability to resist localized corrosion is critical. The material has a critical pitting temperature of approximately 185°F (85°C) in chloride environments, far superior to conventional stainless steels. This makes it a trusted material for essential plant equipment, including:
- Reactors and pressure vessels
- Heat exchangers and condensers
- Storage tanks
- Piping systems
Practical Considerations for Using 2507
While the performance of super duplex steel is unmatched in many areas, its specialized nature requires specific fabrication techniques and a clear understanding of its cost-benefit profile. Proper handling ensures the material delivers its full potential.
Welding and Machining Best Practices
Fabricating this high-performance alloy demands precision. Its two-phase microstructure is sensitive to thermal cycles, making controlled welding procedures essential.
Welding Guidelines ⚙️ Welders must manage heat input carefully, typically within a range of 0.5–2.0 kJ/mm. The temperature between weld passes, known as the interpass temperature, should not exceed 150°C (300°F) to preserve the steel's balanced microstructure.
Selecting the correct filler metal is also critical for a successful weld. Recommended options include:
- 2507/P100 filler metal to ensure a suitable duplex weld structure.
- Nickel alloy fillers, such as the C276 type, to enhance corrosion resistance.
- 6% Molybdenum (Mo) fillers.
Machining this material also presents challenges due to its high strength. Best practices involve using sharp, coated carbide tools and high-quality cutting fluid. Operators can improve machinability by using higher cutting speeds combined with reduced feed rates.
Cost vs. Performance Analysis
Super duplex steel has a higher initial purchase price compared to 2205 duplex or 316L stainless steel. This is due to its enriched content of chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen. However, a simple price comparison is misleading.
A more accurate evaluation uses a Life-Cycle Cost (LCC) analysis. This method considers the total cost over an asset's entire service life.
The LCC Formula:
Initial Cost + Lifetime Maintenance Costs + Replacement Costs – Salvage Value
For long-life assets (15+ years) in critical applications, the higher upfront investment is often justified. The superior corrosion resistance of the alloy minimizes the need for costly maintenance, repairs, and operational shutdowns. In environments where material failure could lead to catastrophic losses, the reliability of a premium alloy provides a clear economic advantage over its entire lifespan.
The title of "ultimate corrosion fighter" for 2507 is well-earned. Its specialized chemistry and microstructure deliver superior strength and unmatched corrosion resistance. These properties make it essential for the most demanding industrial applications. However, its performance relies on correct implementation. For example, a heat exchanger failure occurred when the alloy was welded to a lesser material, causing cracks. This case proves that in critical environments where failure is not an option, the alloy's performance justifies its cost and the need for proper fabrication practices.
FAQ
How does 2507 differ from 2205 duplex steel?
Super duplex 2507 contains higher levels of chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen than 2205 duplex steel. This enriched composition provides superior corrosion resistance and greater mechanical strength. Its higher PREN value confirms its enhanced performance in aggressive chloride environments.
What makes 2507 so resistant to corrosion?
The alloy's high chromium content forms a protective passive layer. Molybdenum and nitrogen enhance this layer, providing exceptional resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. This powerful combination makes it a top performer in chloride-rich settings like seawater.
Can 2507 be used in high-temperature applications?
Engineers specify 2507 for service up to 300°C (572°F). Prolonged exposure above this temperature can alter its microstructure, reducing toughness and corrosion resistance. It maintains good properties in low temperatures down to -50°C (-58°F), making it versatile for many industrial processes.
Is 2507 super duplex steel expensive?
The initial material cost for 2507 is higher than for standard stainless steels. However, its exceptional durability reduces long-term maintenance and replacement needs. This makes it a cost-effective choice for critical, long-life applications where reliability is paramount.
See Also
Mastering Pass Partition Plate Welding: Expert Techniques for 2025 Success
Achieving Optimal Results: Steel Processing for Heat Exchange Applications
Uncovering Unexpected Solutions: Troubleshooting Sulfur Recovery Catalyst Effectively
Essential Guide: Frame Plate Kits for Automotive Reinforcement Beginners
Exploring Molybdenum High-Temperature Furnaces: Key Insights for 2025